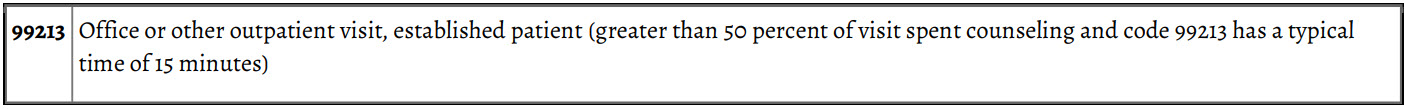While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a more complicated matter. This Coding Fact Sheet will provide you with a guide to coding for pediatric hearing screening. While we have provided you with some suggested codes, it should be noted that payer recognition of codes might vary. Most plans are required to cover hearing screen services under the Affordable Care Act, however, that may still vary. The codes listed here are commonly reported not an exhaustive list.
International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10 CM) Codes
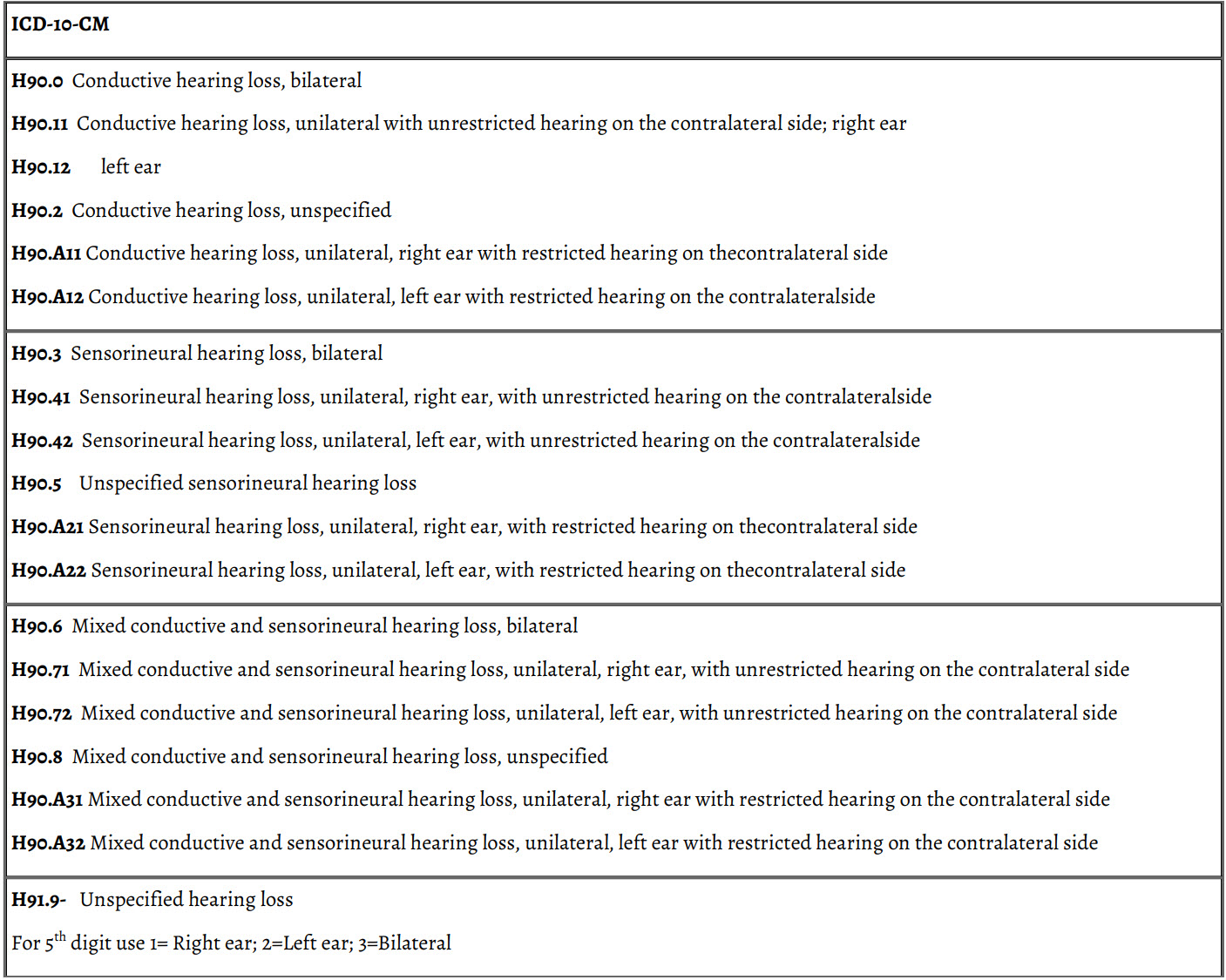
Hearing Loss
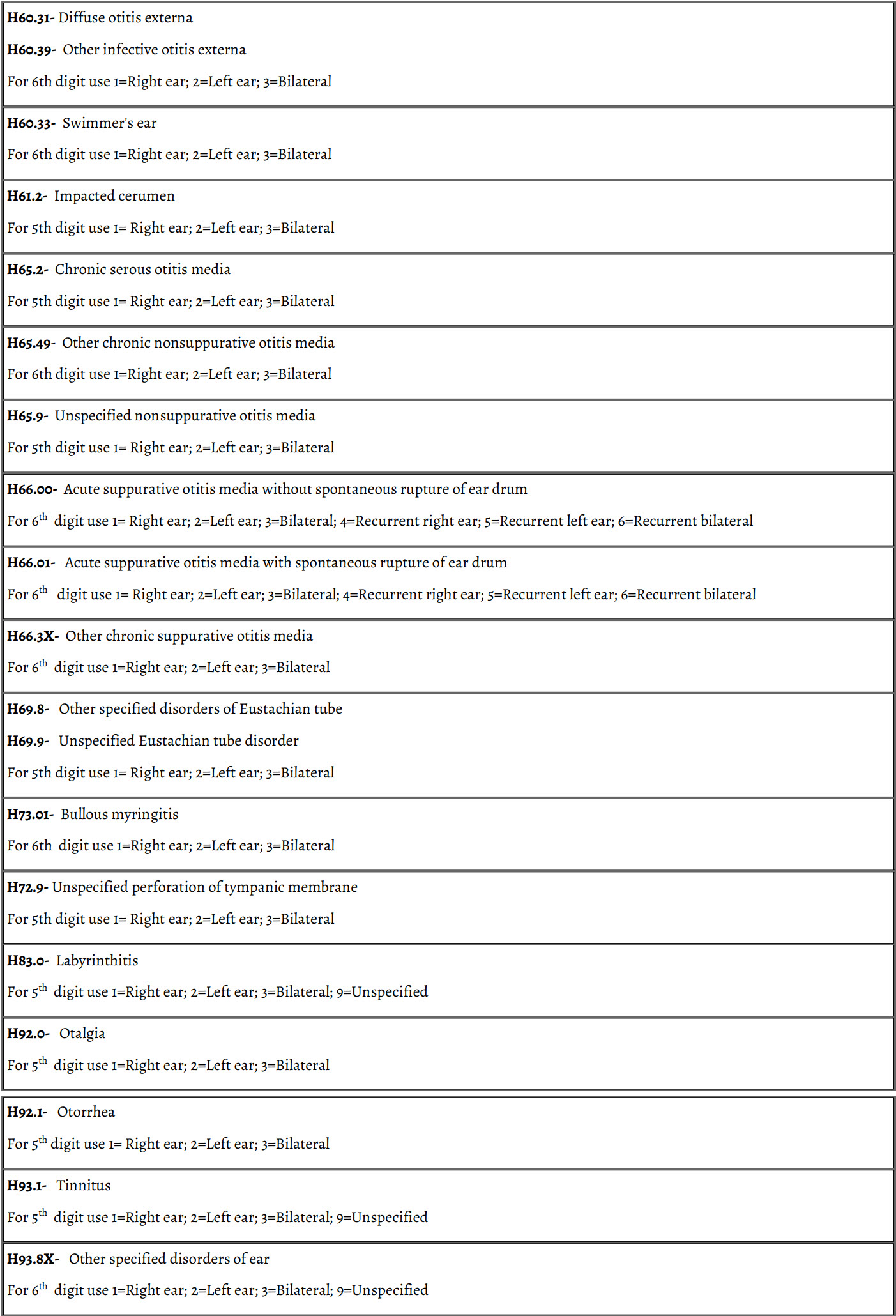
Other Diagnosis Codes Related To Hearing Loss
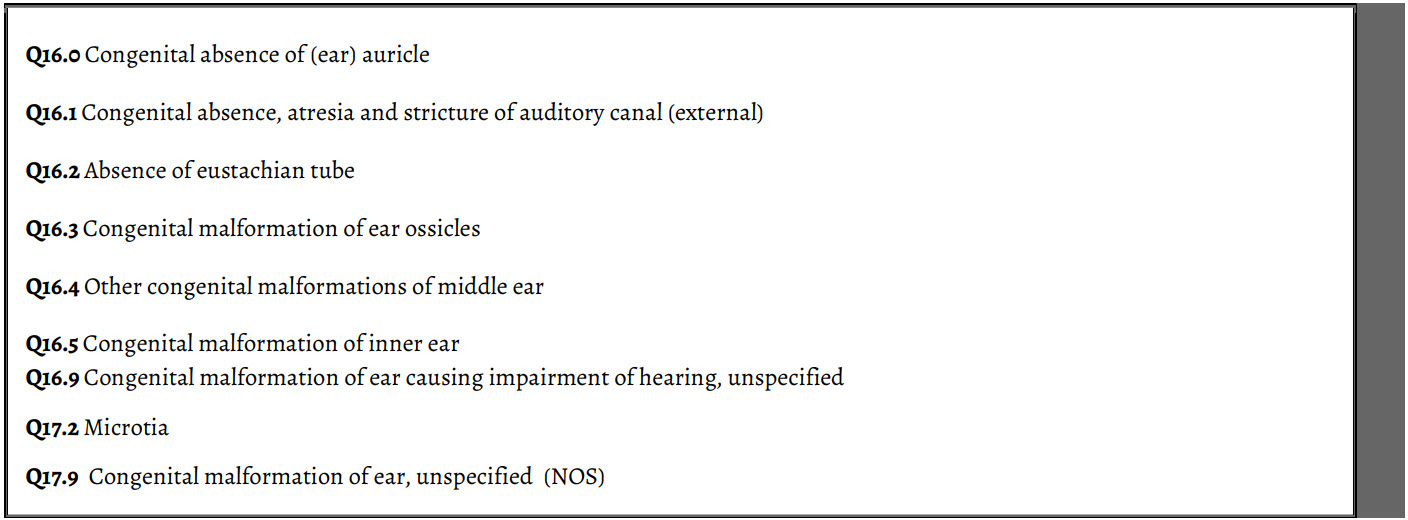
Congenital Anomalies
Injury and Poisoning
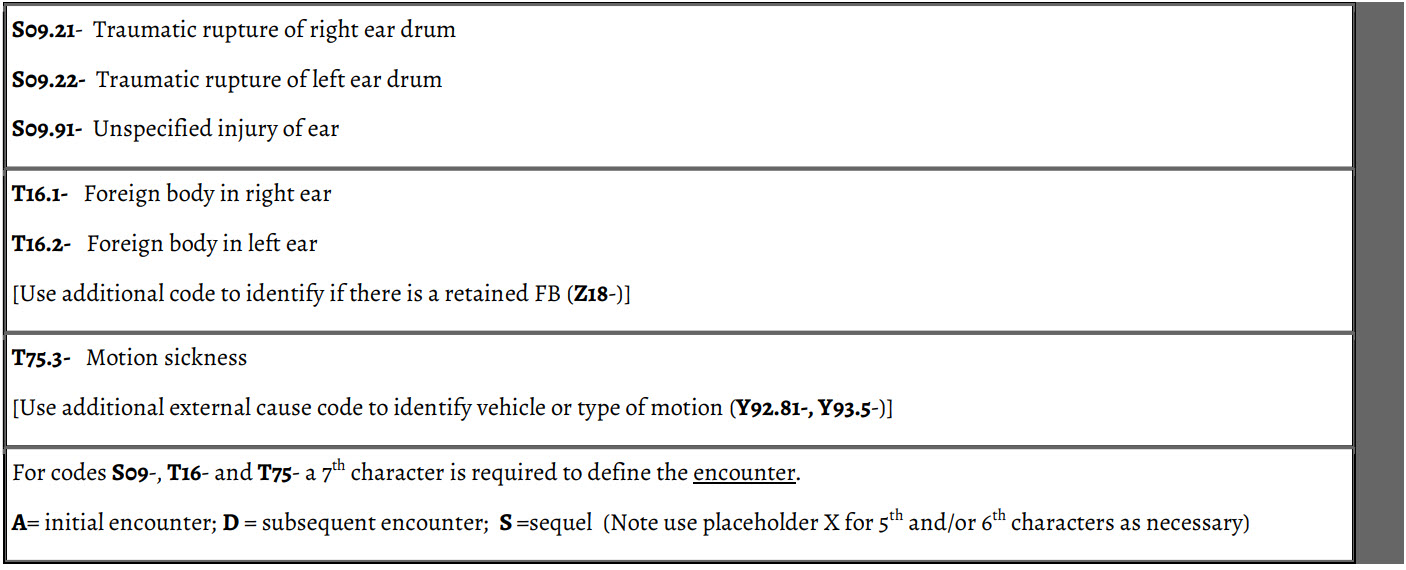
Symptoms, Signs, and ILL-Defined Conditions
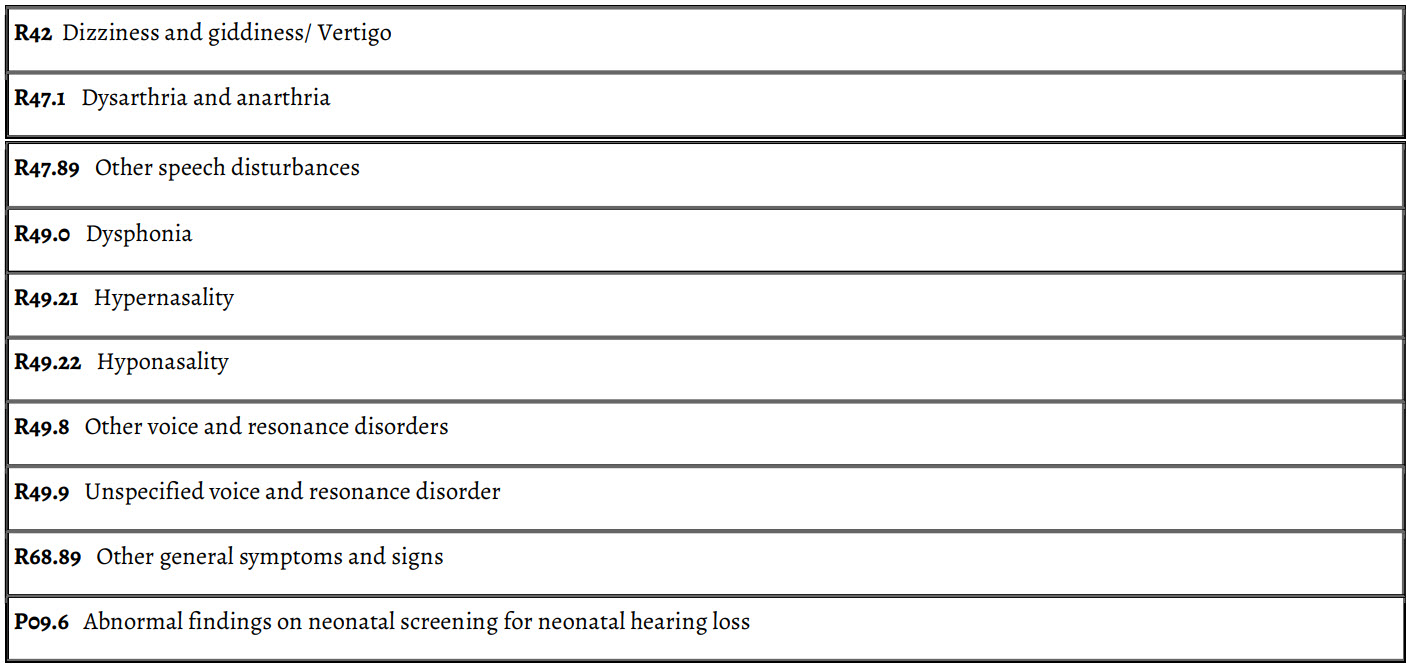
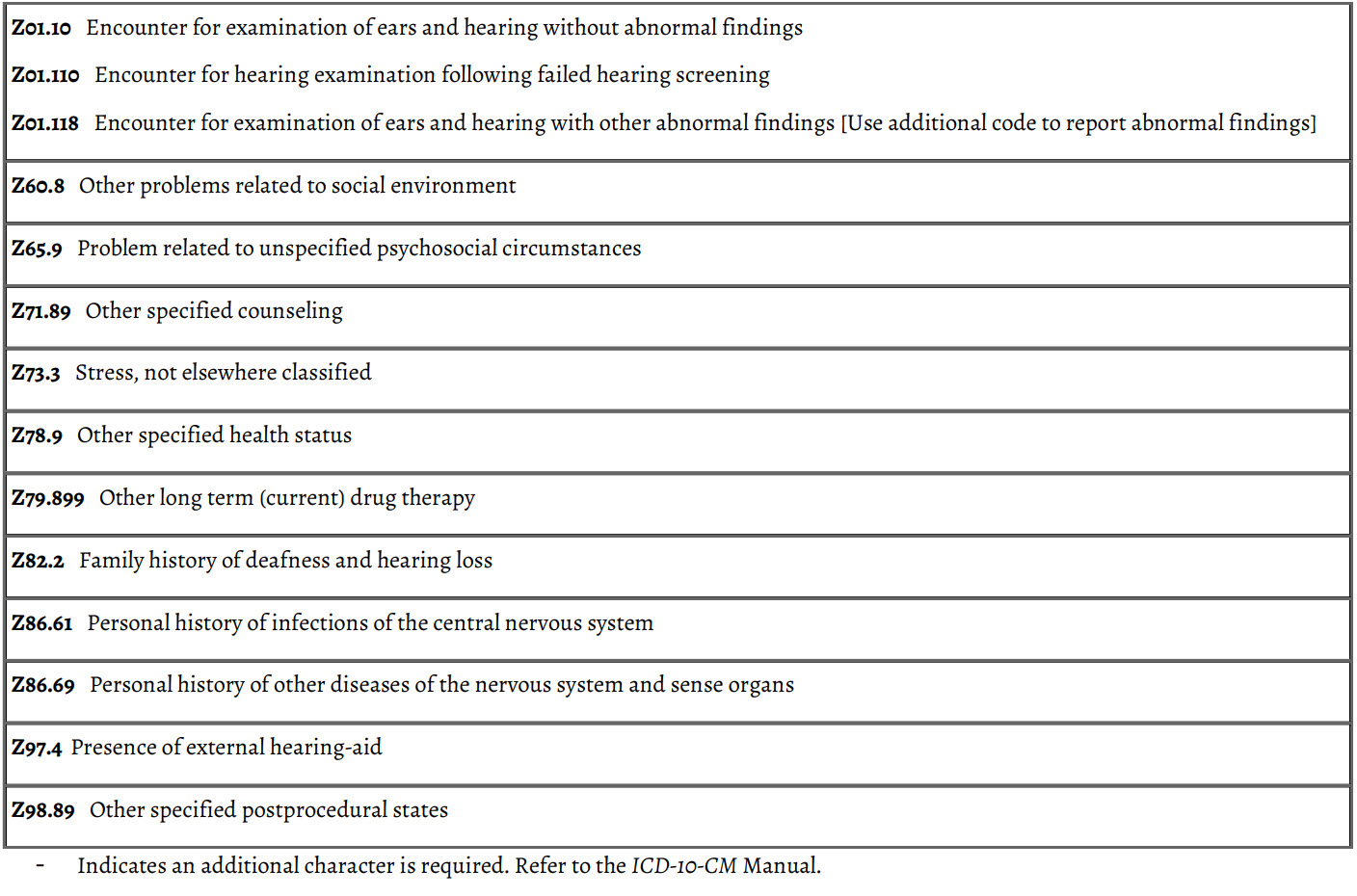
Z Codes
Z codes represent reasons for encounters. Categories Z00–Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury, or external cause classifiable to categories A00–Y89 are recorded as 'diagnoses' or 'problems'. This can arise in 2 main ways.
(a) When a person who may or may not be sick encounters the health services for some specific purpose, such as to receive limited care or service for a current condition, to donate an organ or tissue, to receive prophylactic vaccination (immunization), or to discuss a problem is in itself not a disease or injury.
(b) When some circumstance or problem is present which influences the person’s health status but is not in itself a current illness or injury.
(c) When a social determinant of health is identified during an encounter and it is either addressed or shown to complicate the encounter, it should be coded.
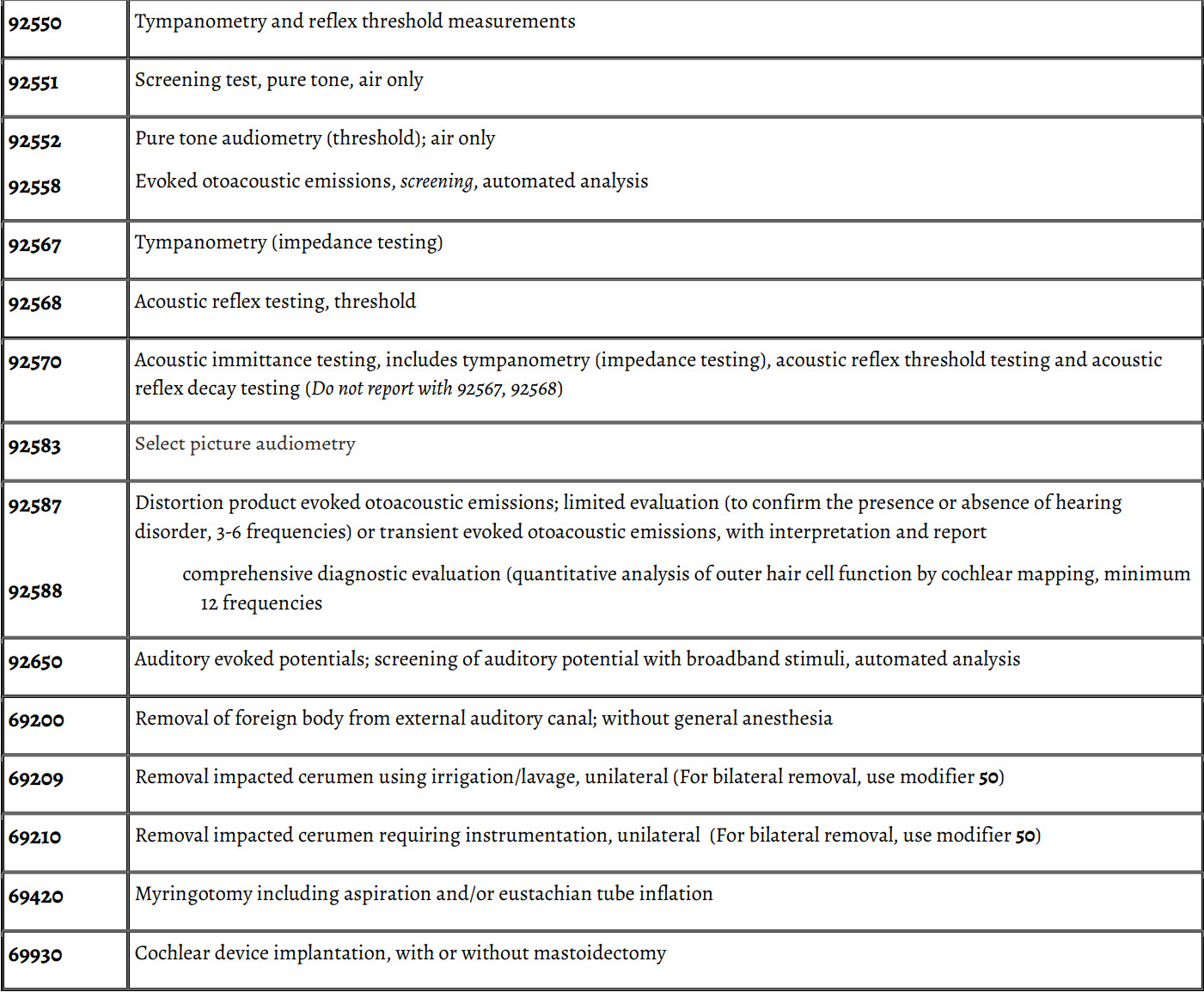
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) Codes
The audiometric tests listed below require the use of calibrated electronic equipment, recording of results, and a report with interpretation. Hearing tests (such as whispered voice, tuning fork) that are otorhinolaryngologic evaluation and management services are not reported separately. All services listed are bilateral. Use modifier 52 if a test is applied to one ear only.
Health and Behavior Assessment/Intervention Codes
These codes are not reported by a physician.
Assessment

The focus of the assessment is not on mental health but on the biopsychosocial factors important to physical health problems and treatments.
Intervention
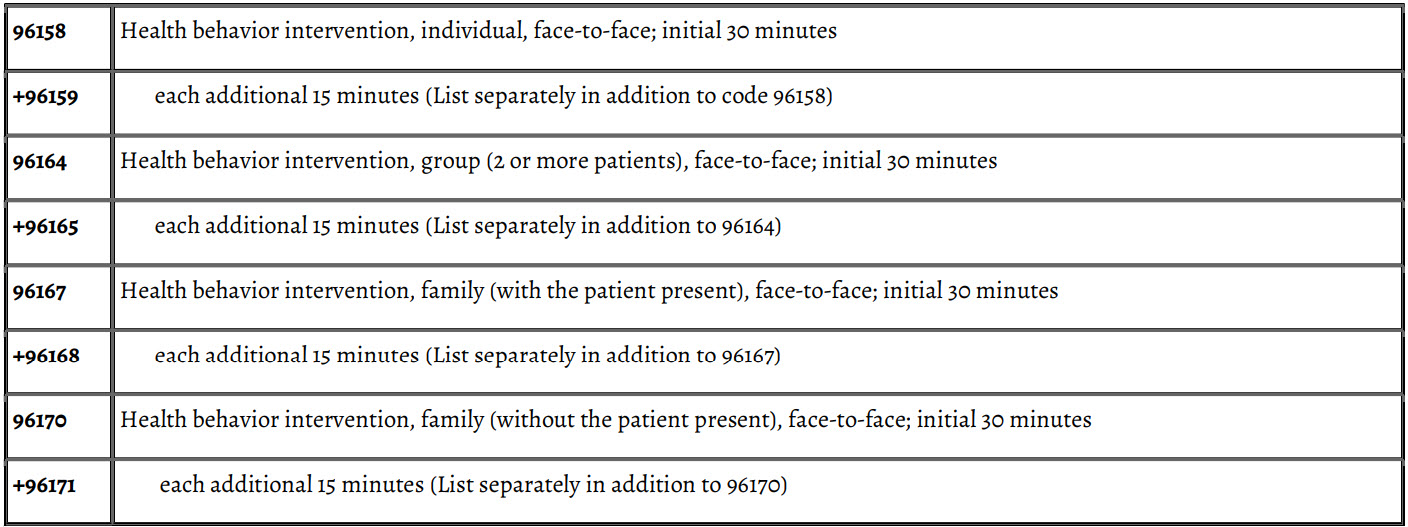
The focus of the intervention is to improve the patient's health and well-being utilizing cognitive, behavioral, social, and/or psychophysiological procedures designed to ameliorate the specific hearing-related problems.
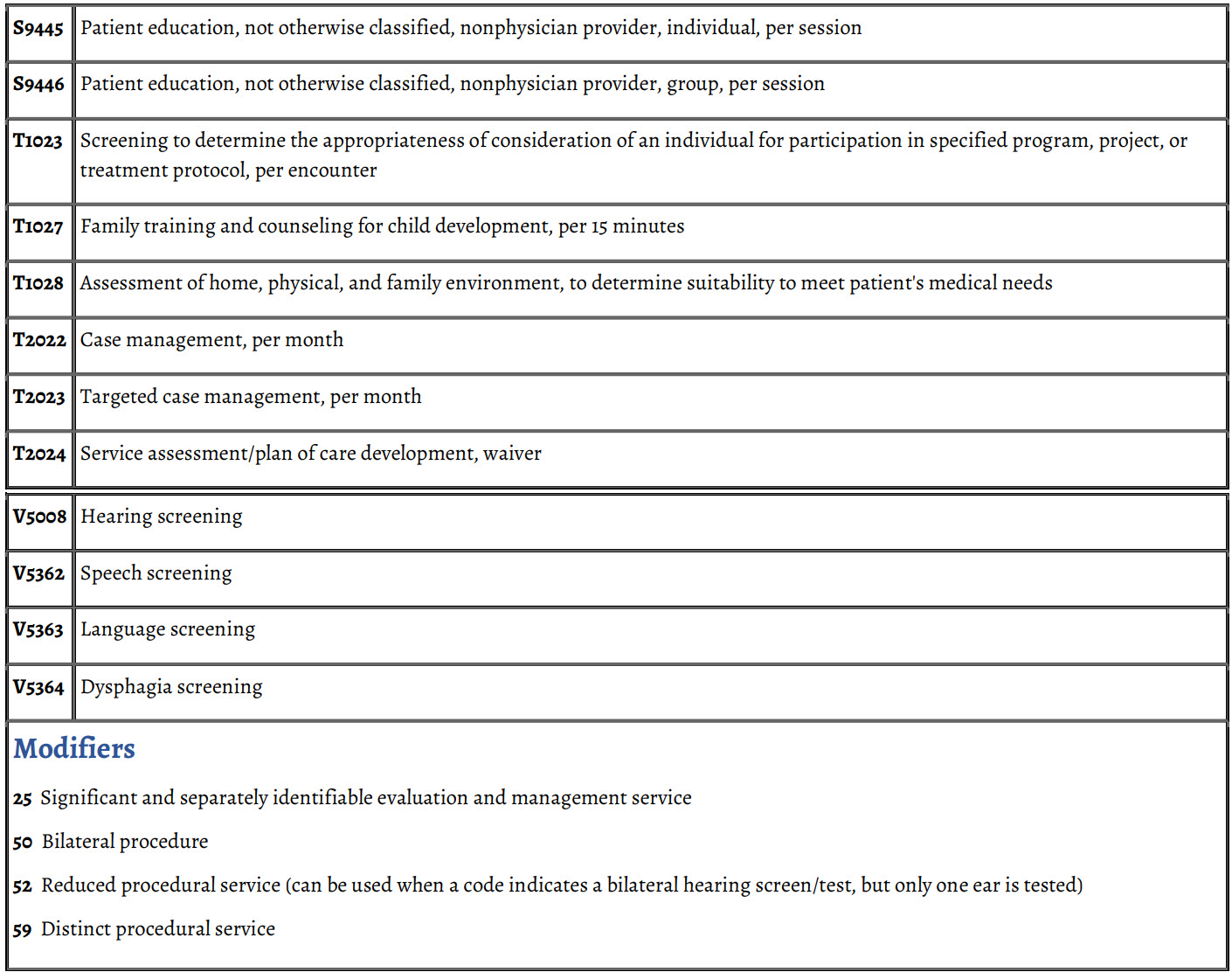
Healthcare Common Procedural Coding System (HCPCS) Codes
CPT codes are also known as Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) Level I codes. The HCPCS also contains Level II codes. These Level II codes (commonly referred to as HCPCS "hick-picks" codes) are national codes that are included as part of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) standard procedural transaction coding set along with CPT codes.
HCPCS Level II codes were developed to fill in the gaps in the CPT nomenclature. While they are reported in the same way as a CPT code, they consist of one alphabetic character (A-V) followed by four digits. In the past, insurance carriers did not uniformly recognize HCPCS Level II codes. However, with the advent of HIPAA, carrier software systems must now be able to recognize all HCPCS Level I (CPT®) and Level II codes.
HCPCS Hearing Services Codes
Vignettes
Last Updated
06/26/2025
Source
American Academy of Pediatrics