Congenital heart defects represent the most common birth defect in the United States (US), af fecting 1 in 100 children born. They account for 6% of all infant deaths and 15% of all pediatric hospitalization expenses in the US each year. Advancements in surgical and catheter-based interventions and medical therapies for congenital heart disease (CHD) have dramatically increased the survival rates for infants and children, resulting in more than 90% of children with CHD surviving into adulthood. The growing population of children and adults living with CHD requires equitable access to multidisciplinary, life-long care. Geographic location, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status should not impact access to that care.
Access to Care Framework for Congenital Heart Disease
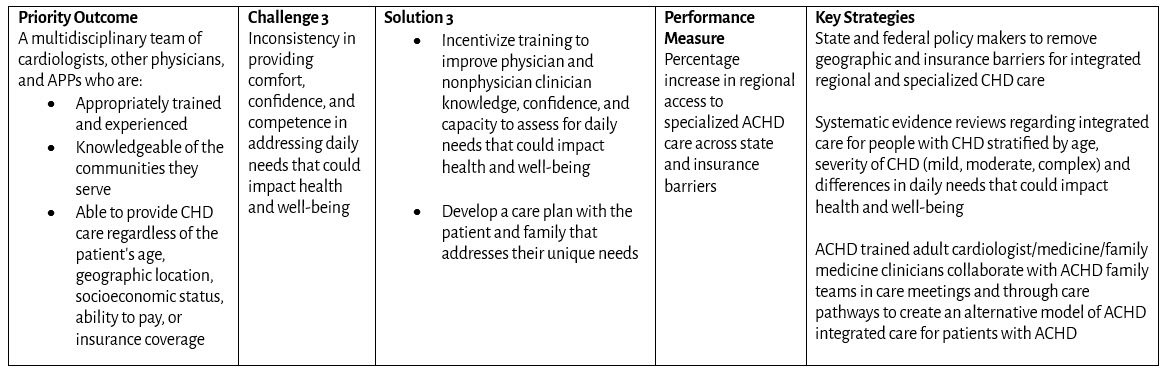
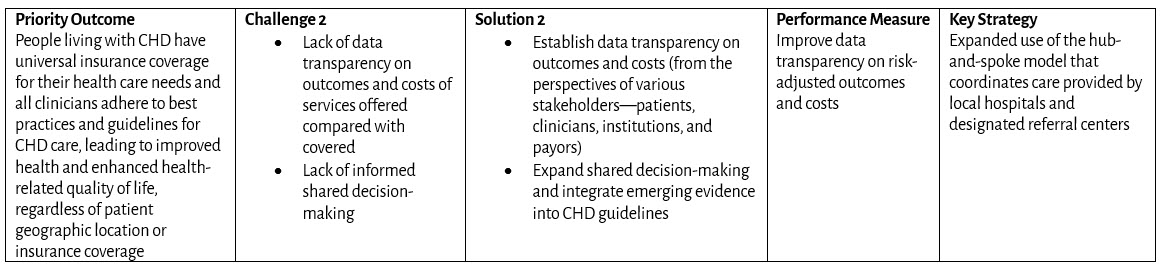
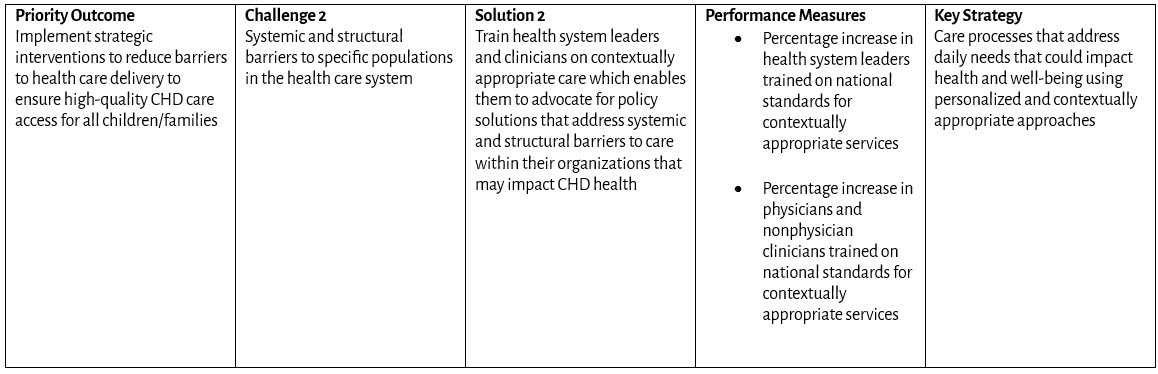
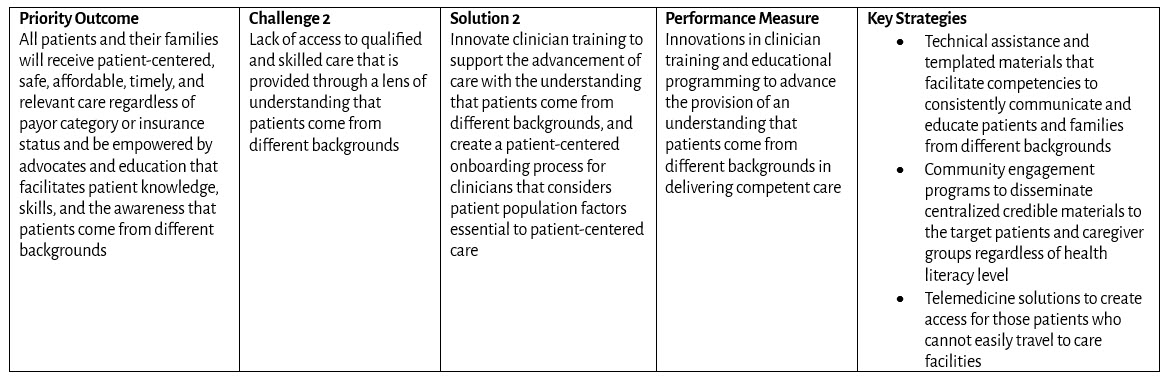
Goal: All infants, children, adolescents, and adults living with congenital heart disease (CHD) in the United States have access to comprehensive, high-quality, congenital cardiology care across their lifespan.
Priority Outcomes: What changes in behavior, condition, or status are required?
Challenges: What are the public health challenges that create barriers to congenital cardiology care?
Solutions: What public and private sector initiatives will advance public health outcomes for CHD?
Performance Measures: How do we measure progress toward outcomes?
Key Strategies: Which programs will drive results?
Amplification and Diversification of Workforce
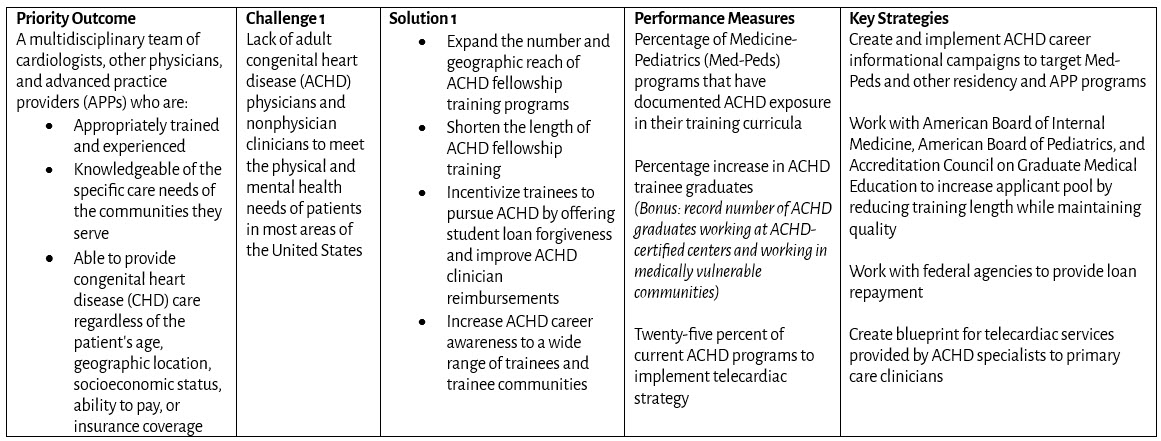
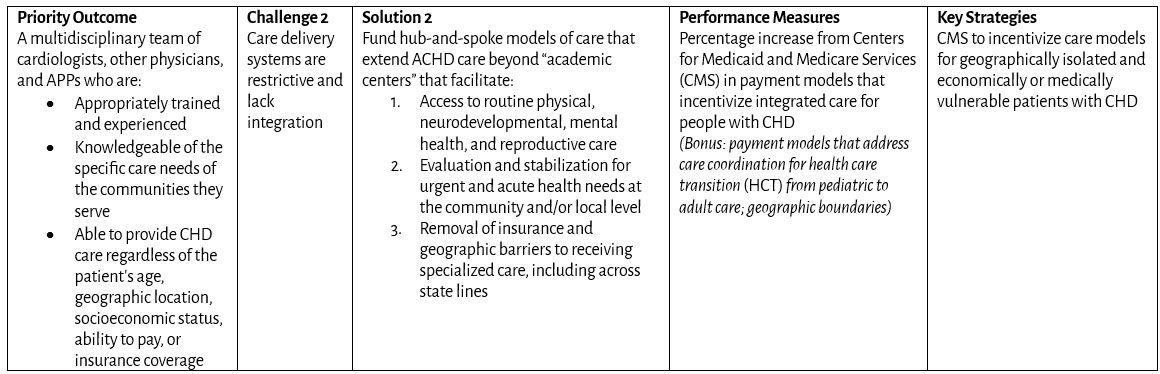
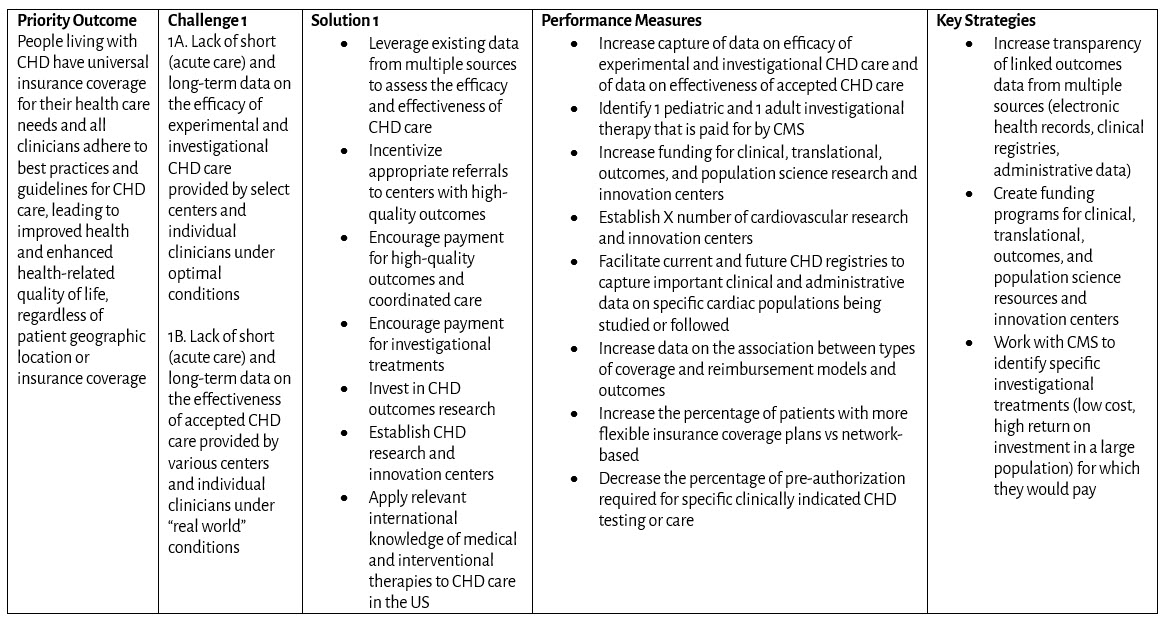
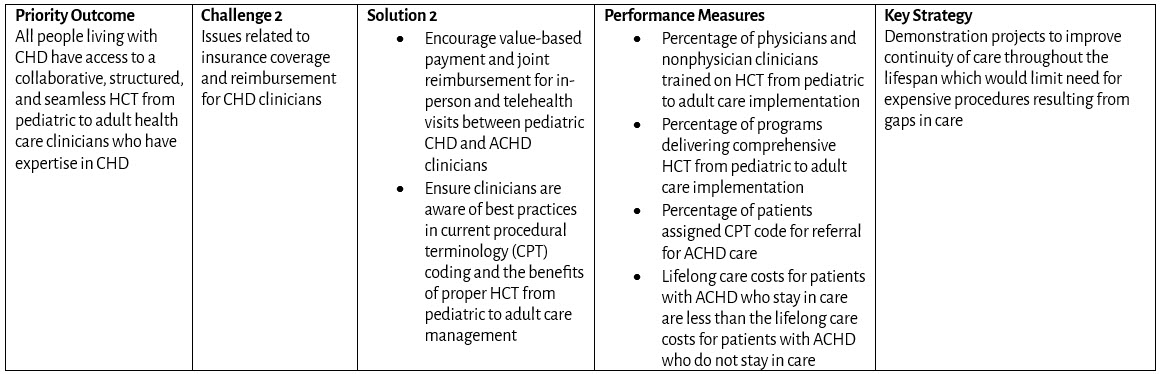
Coverage and Reimbursement

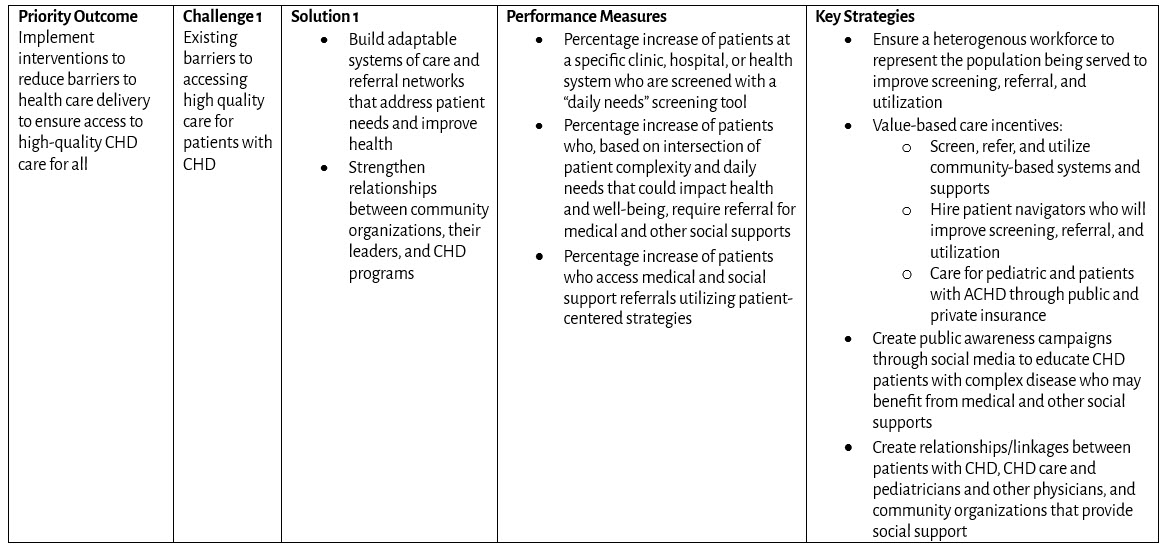
Barriers to Access to Care Based on Daily Needs that Could Impact Health and Well-being
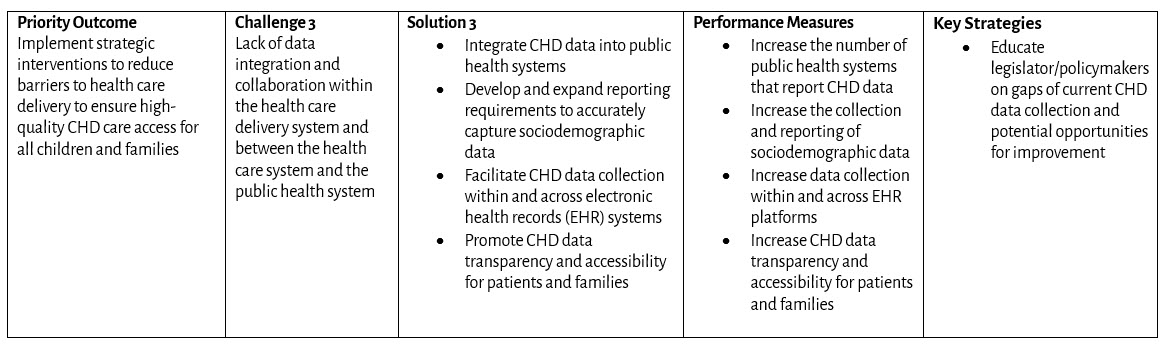
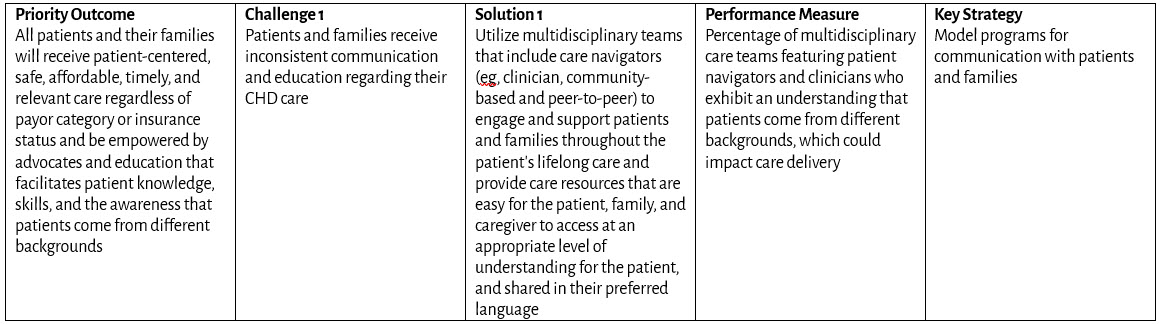
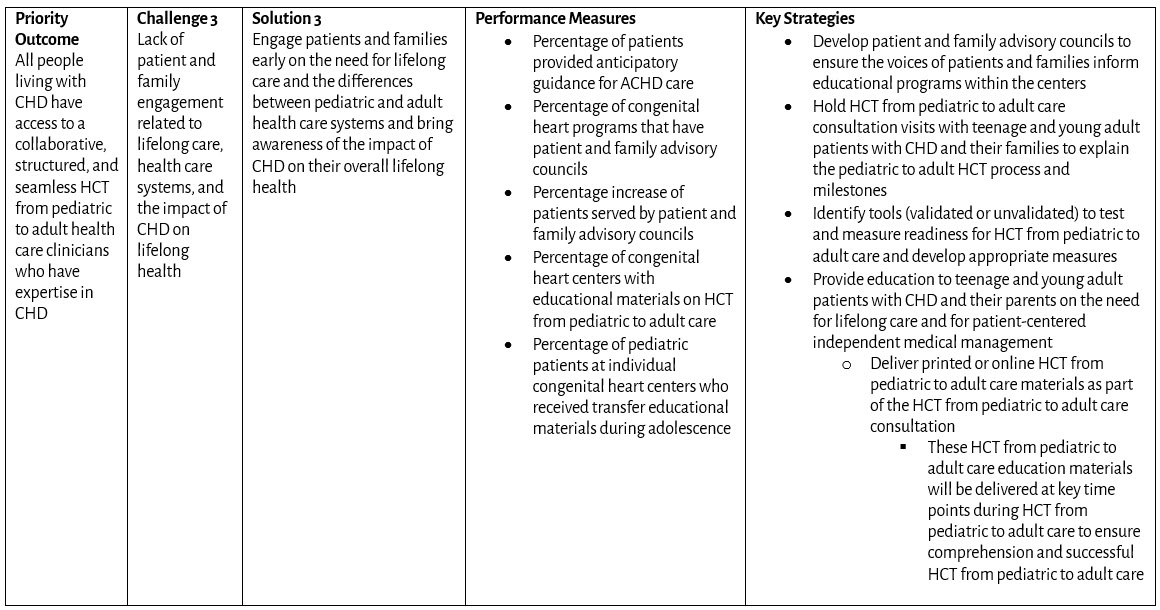
Patient and Family Engagement
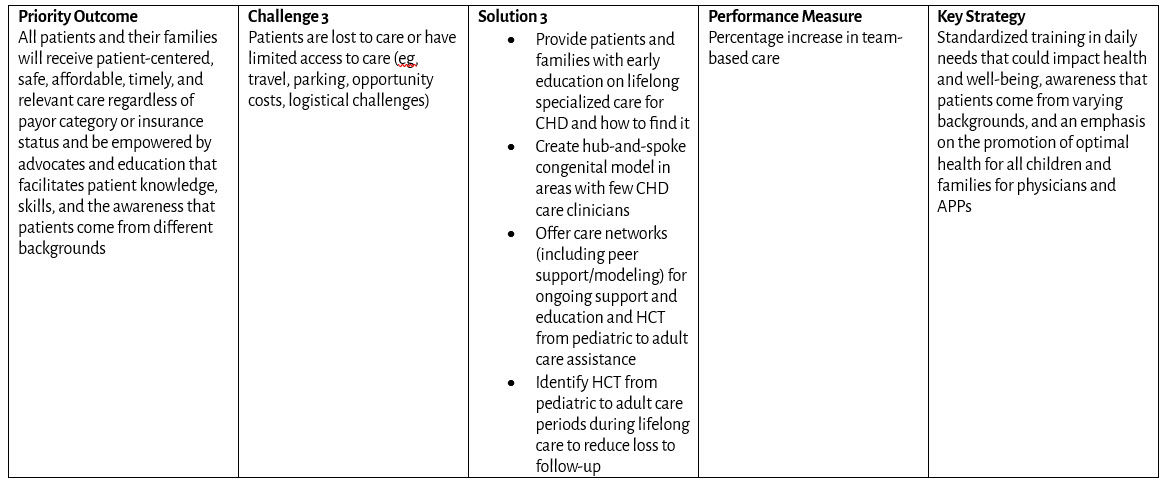
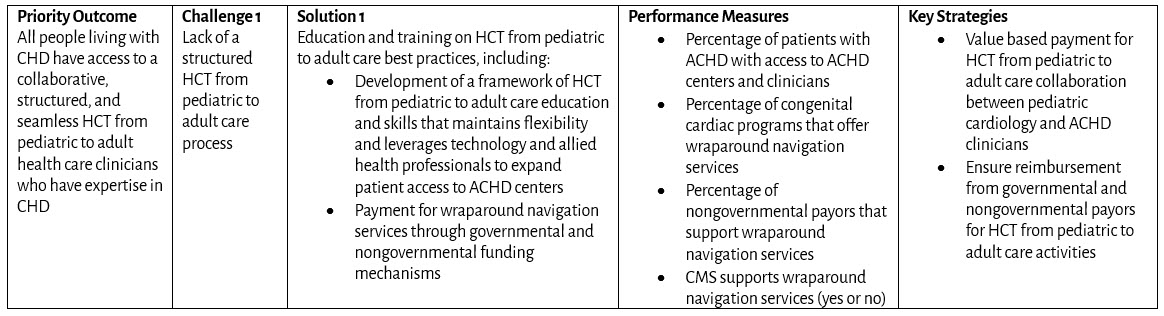
Health Care Transition from Pediatric to Adult Care and Transfer
The Congenital Health Public Health Consortium (CHPHC) is supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The outputs of the CHPHC are solely the responsibility of the CHPHC and do not necessarily represent the official views of, or an endorsement by, the member organizations of the CHPHC, CDC/HHS, or the U.S. Government.

Last Updated
01/22/2026
Source
American Academy of Pediatrics