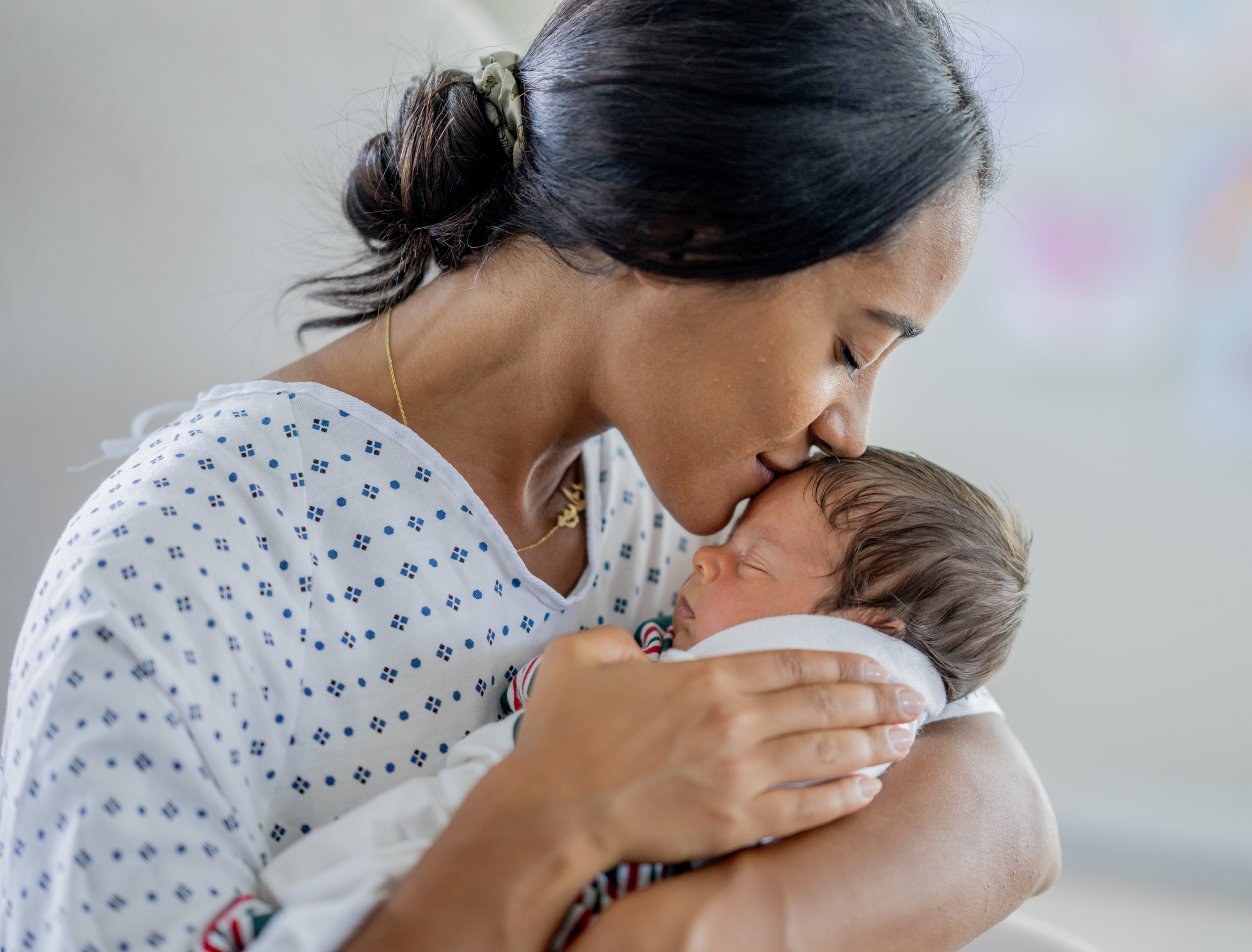


Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is on the rise, particularly among individuals of childbearing age. Perinatal transmission is when HCV is passed from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy or delivery—is the most common route of HCV infection in children. Recognizing this growing concern, the CDC has identified perinatal HCV as an emerging threat through its Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Mothers and Babies Network (SET-NET)
Perinatal Hepatitis C Overview
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is curable in more than 95% of cases, making early detection and treatment critically important. This toolkit provides shareable educational resources on perinatal hepatitis C, including downloadable materials and social media graphics for both clinicians and families. These resources were developed in collaboration with AAP state chapters and local health departments as part of a CDC-funded project addressing emerging health threats affecting infants, children and families. Additional information about participating states and the CDC’s Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Mothers and Babies Network (SET-NET) can be found in the partner resources section below.
Clinician and Family Educational Resources

Clinical Resources
Access downloadable resources for pediatric and family clinicians including information sheets, tip sheets and more.

Social Media
Access social media graphics for clinicians and families on perinatal hepatitis C, including screening, testing and treatment.

AAP Redbook
Access AAP’s redbook online or downloadable and interactive tools to address perinatal hepatitis c in your practice. (login required)
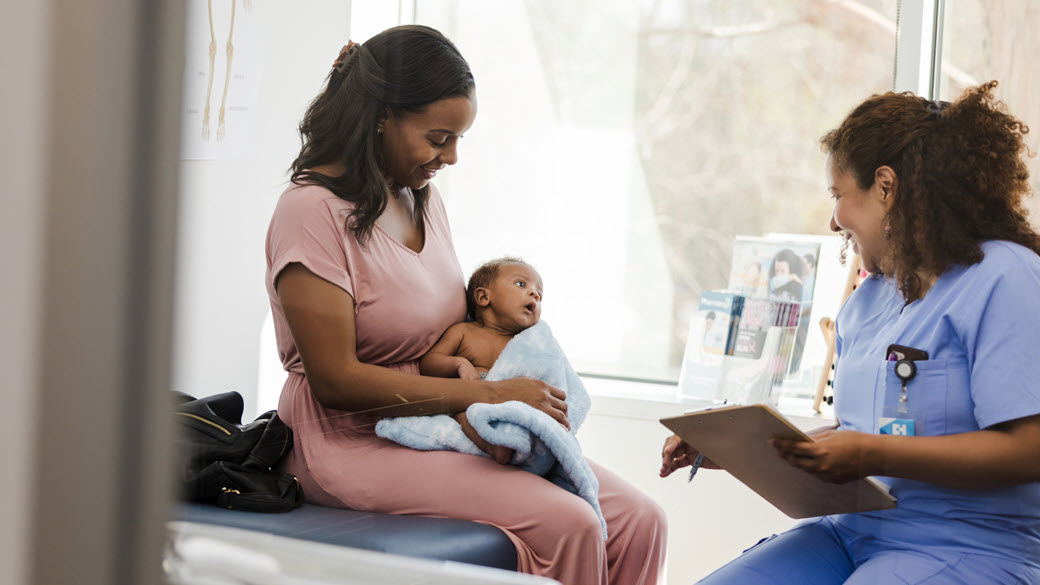
Family Resources
Access downloadable educational resources to share with families in your practice and community.

HealthyChildren.org
Access downloadable and shareable articles for families to increase awareness and education on hepatitis C.
Journals and Periodicals
Access AAP's peer-reviewed articles and evidence-based summaries on hepatitis C.
Partner and Support Organization Resources

AAP Chapter Resources
Access local and state specific resources from AAP chapters on perinatal Hepatitis C. Including resources developed from the Arizona and Pennsylvania chapters work with 'local health departments sites to address perinatal Hepatitis C in their states.

American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)
Access additional education and training resources on perinatal HCV from ACOG.
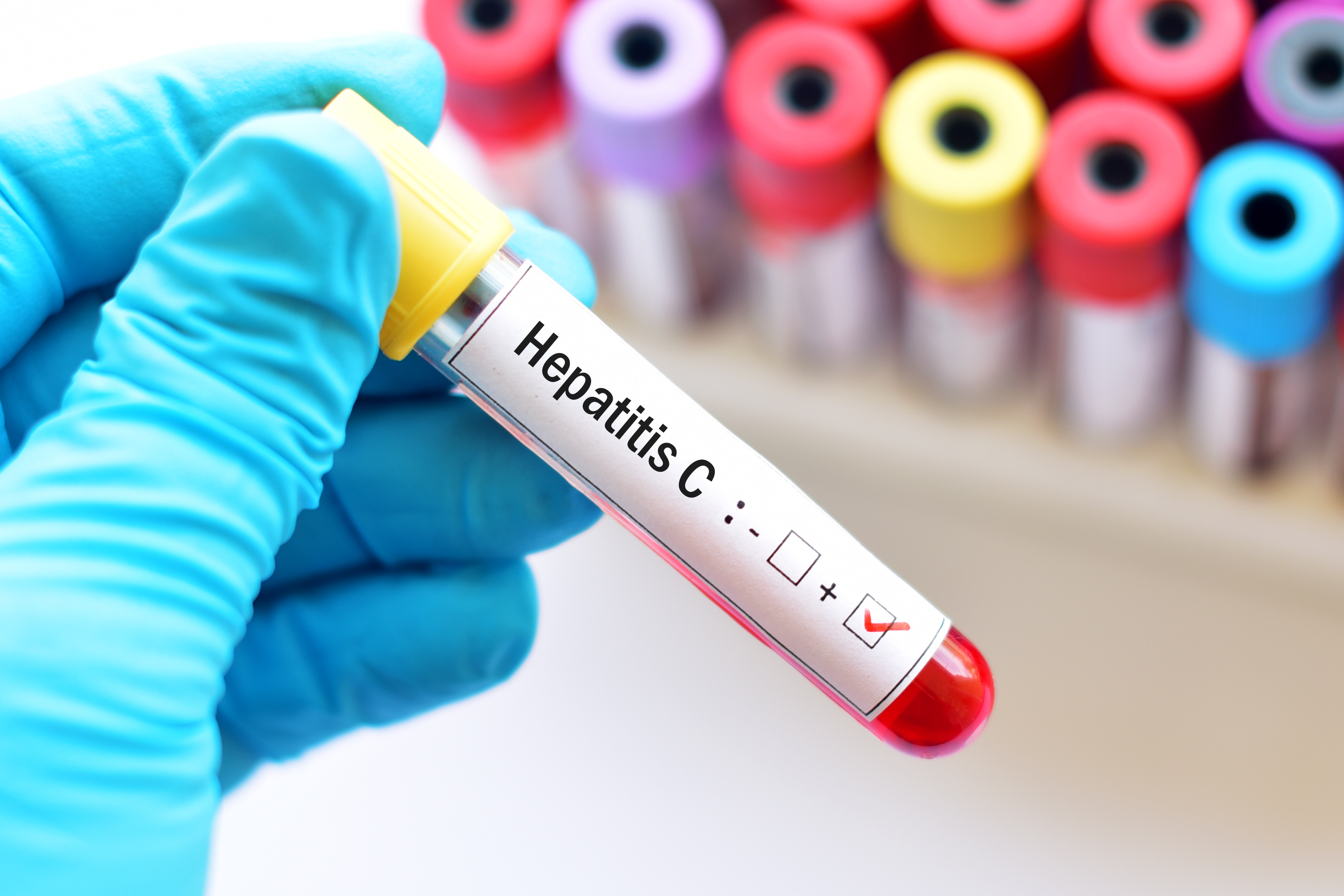
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Access CDC's clinical tools and resources to help address HCV in your practice or community including guidance on screening, testing, managing and treating HCV.

AASLD/IDSA
Access comprehensive and frequently updated resources from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America, including recommendations for testing managing and treating Hepatitis C

U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF)
Access universal screening recommendations on HCV from USPSTF.

MotherToBaby
Mother to Baby provides resources on medication safety in pregnancy and lactation, including information on HCV treatments.
NIH Liver Tox
Resource to support clinicians dealing with hepatotoxicity in perinatal care.
National Viral Hepatitis Roundtable (NVHR)
Access information and resource from NVHR on their viral hepatitis initiatives.
Additional Resources
CDC Surveillance for Emerging Threats to Mothers and Babies Network (SET-NET)
Perinatal Hepatitis C
Emerging Threats
This project is supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of a financial assistance award totaling $350,000 with 100 percent funded by CDC/HHS. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC/HHS, or the U.S. Government
Last Updated
08/06/2025
Source
American Academy of Pediatrics