Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). It is one of the most common viral hepatitis diseases found in the US and can result in acute or chronic disease. The most common route of transmission for children infected with HCV is perinatally. Discover essential information about perinatal HCV, including screening, testing and treatment below.
Perinatal Hepatitis C Overview
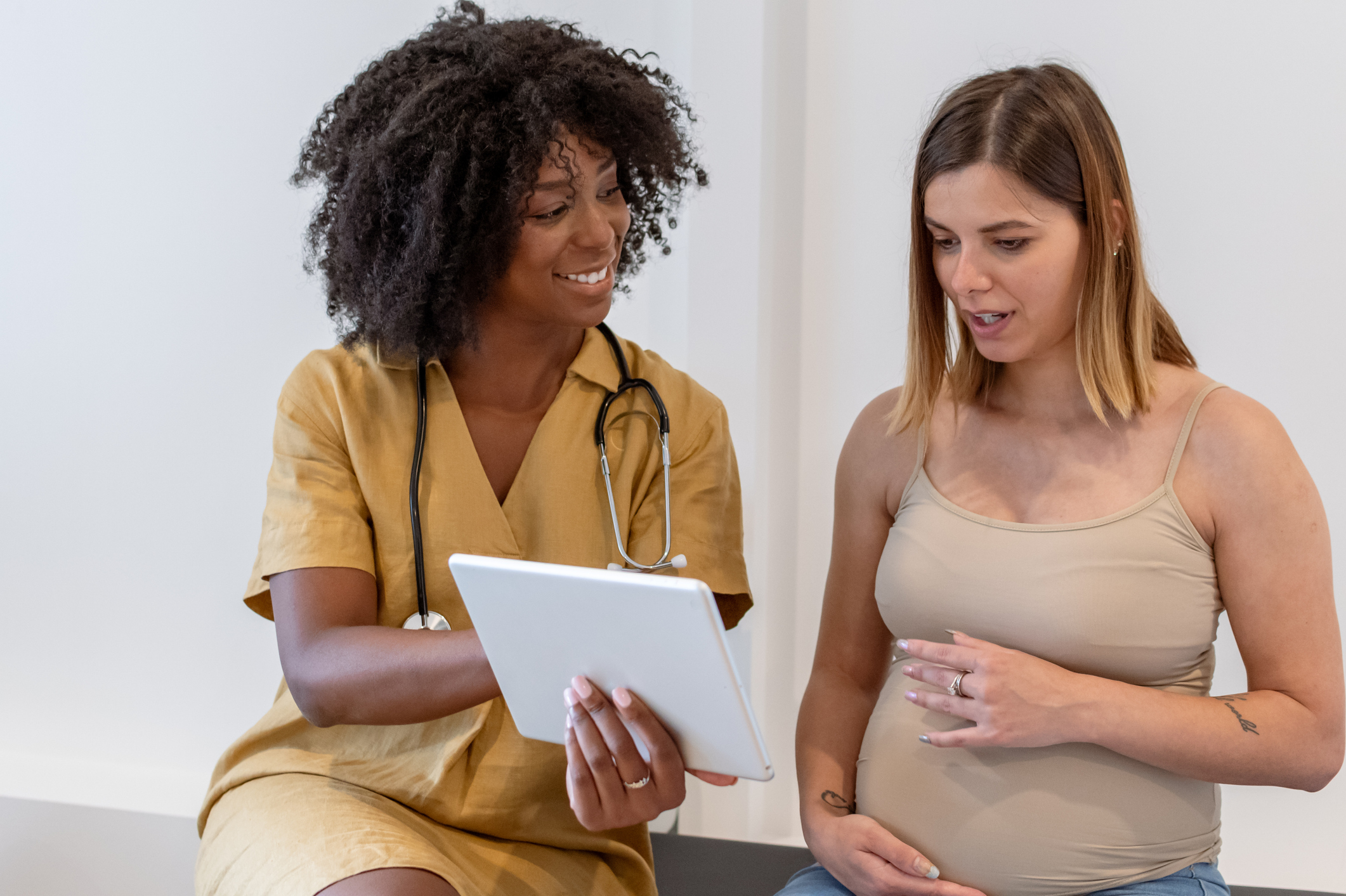
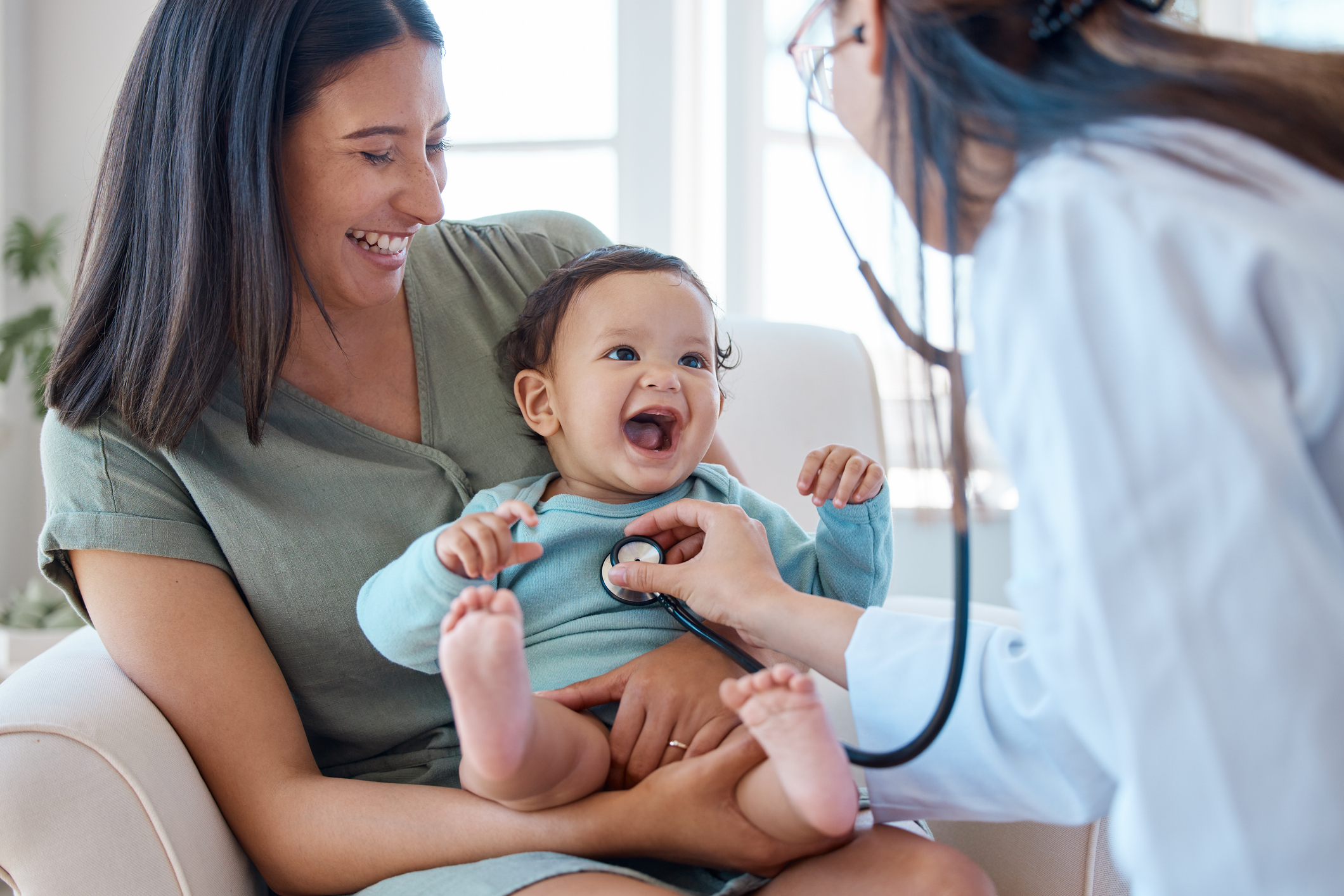
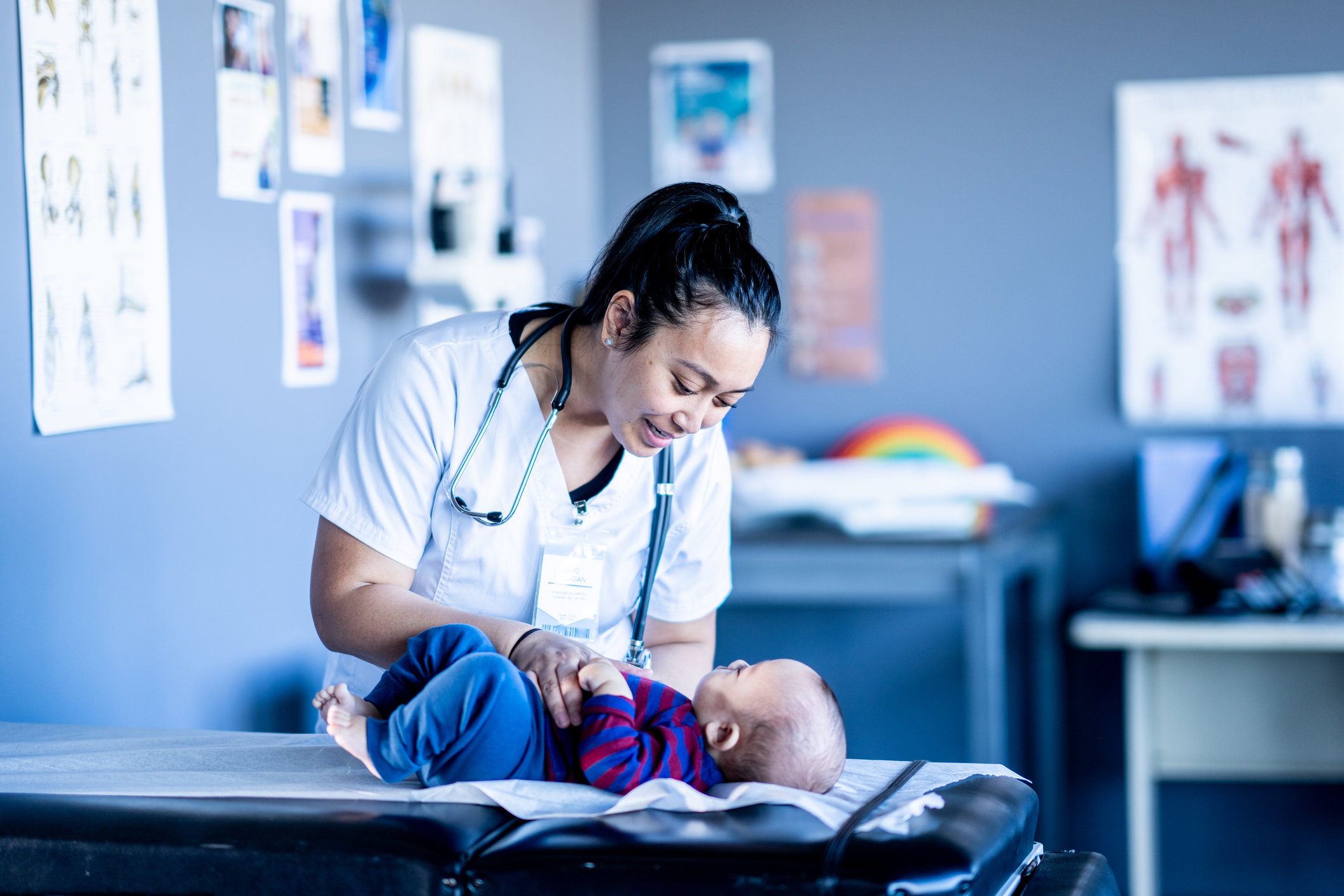
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections are on the rise, including among infants and children, and can lead to serious complications such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Transmission occurs through contact with infected blood, sexual contact, shared needles, and perinatally—from mother to child during pregnancy or delivery. Because many individuals with HCV are asymptomatic, they may be unaware of their infection and the potential for perinatal transmission.
To address this, the CDC recommends universal HCV screening during every pregnancy. Infants exposed perinatally should be tested between 2 to 6 months of age using a nucleic acid test (NAT) for HCV RNA. If testing is delayed, children aged 7–17 months should still receive NAT, while those 18 months or older should undergo anti-HCV antibody testing followed by reflex NAT if the antibody test is reactive. Children who test positive should be referred to a pediatric infectious disease or HCV specialist for ongoing care. Encouragingly, hepatitis C is curable in over 95% of cases with appropriate antiviral treatment.
Professional Tools and Resources
Partner Resources
Resources for Families
Hepatitis C: What Parents Need to Know
How do Children Get Hepatitis?
Get Involved
Section on Infectious Disease
Committee on Infectious Diseases
This project is supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of a financial assistance award totaling $350,000 with 100 percent funded by CDC/HHS. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC/HHS, or the U.S. Government.
Last Updated
08/05/2025
Source
American Academy of Pediatrics